马里兰大学案例:集成流体电路机械手-可玩超级玛丽

简介
此研究由美国马里兰大学Ryan D. Sochol 教授领导的BAM实验室完成。
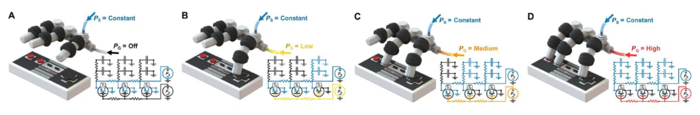
他们使用了激光直写的3D微流体技术、多材料激光直写、3D打印软体机器人等技术,配合法国Fluigent的压力泵(用于机械手段精细驱动),制作了一款可以玩《超级玛丽》的机械手,于2021年发了一篇SCI论文,并被美国CBS News专门采访报道。
论文:Hubbard, J. D. et al. Fully 3D-printed soft robots with integrated fluidic circuitry. Sci. Adv. 7, (2021).



相关文献:
[1]. Hubbard, J. D. et al. Fully 3D-printed soft robots with integrated fluidic circuitry. Sci. Adv. 7, (2021).
[2]. Sochol, R. D. et al. 3D printed microfluidic circuitry via multijet-based additive manufacturing. Lab Chip 16, 668–678 (2016).
相关实验室网站:
Keyser lab website: http://people.bss.phy.cam.ac.uk/~ufk20/
Cambridge Cavendish Laboratory website: https://www.phy.cam.ac.uk/